Презентация - The noun
просмотров
Текст этой презентации
Слайд 1

The noun
a word expressing substance in the widest sense of the word
Слайд 2
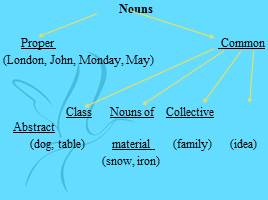
Nouns Proper Common
(London, John, Monday, May) Class Nouns of Collective Abstract (dog, table) material (family) (idea) (snow, iron)
Слайд 3
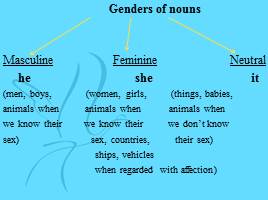
Genders of nouns Masculine Feminine Neutral he she it
(men, boys, (women, girls, (things, babies,
animals when animals when animals when
we know their we know their we don’t know
sex) sex, countries, their sex) ships, vehicles when regarded with affection)
Слайд 4

Most nouns describing people have the same form whether they are male or female (teacher, student). Some nouns have different forms: actor – actress groom – bride waiter – waitress host – hostess widower – widow steward – stewardess prince – princess hero – heroine duke – duchess king – queen monk – nun heir - heiress
Слайд 5

Noun-forming suffixes:
-er, -or, -ar, -est, -ness, -ism, -ess, -(a)ion, -tion, -sion, -hood, -dom, -ship, -ment, -ance, -ence, -ty, -ity, -ure,
-age, -y, -ee, -ian, -al, -sis, -cy The most common prefixes:
re-, co-, dis-, mis-, over-, under-, sub-, inter- Compound nouns:
one word (classroom), two words (CD player), hyphen (game-tester)
Слайд 6

Nouns Countable Uncountable
denote things that denote things we
can be counted can’t count can take singular and always take singular plural verbs; verbs;
go with –a,-an,-my/his/ don’t go with –a,-an,
her/your/its/our/their, one/two…, these/ -this/these/that/those those
Слайд 7

Countables can be used with Uncountables can be used with
Many, few, a few, a couple of, several, a number of, both, a lot of, lots of, plenty of, some, any, no Much, little, a little, a good deal of, a large amount of, a small quantity of, a lot of, lots of, some, any, no
We use –a, -an, one/two… with such uncountables as tea, coffee, etc. when we order smth. in a restaurant, etc.
Слайд 8

Some problems with uncountables
Some nouns are uncountable in English but countable in Russian: advice (совет), news (новости), money (деньги), information (сведения), progress (успех), travel (путешествие), trouble (проблема), hair (волосы), success (успех), toast (гренки), applause (аплодисменты), knowledge (знания), evidence (признак, свидетельство),spaghetti (спагетти), failure (неудача), fruit (фрукты), etc.
Слайд 9

Some problems with uncountables
Some nouns can be used as countable or uncountable with a difference in meaning: a glass(стакан), glasses(очки), a paper(газета), papers(документы), a hair(волосина), an iron(утюг), a wood(лес), times(разы), experiences(события), works(произведения), a chicken ( the animal), a toast (тост), a help (помощник), a gossip (сплетник), cheeses/fruits and other words denoting different sorts of a given material or food, etc.
Слайд 10

Some problems with uncountables
Many uncountable nouns can be made countable by adding a partitive: a piece of, a bottle of, a sheet of, a box of, a slice of, a loaf of, a bit of, a kilo of, a tube of, a plate of, etc. Always look it up in the dictionary!
Слайд 11

Nouns are made plural by adding:
-s to the noun
-es to nouns ending in –s, -ss, -x, -ch, -sh, -z
-ies to nouns ending in consonant + y
-es to nouns ending in consonant + o ( But –s if they are abbreviations (photos, kilos, autos, etc.), musical instruments (pianos), proper nouns (Eskimos). Some nouns ending in –o can take either –s or –es ( buffalo, mosquito, volcano, tornado, zero, etc.)
-ves to some nouns ending in –f/-fe (calves, halves, knives, leaves, selves, thieves, wolves, wives, etc.) But: beliefs, chiefs, cliffs, handkerchiefs, scarfs/scarves, hoofs/hooves (копыто), roofs, safes)
Greek or Latin suffixes ( basis- bases, crisis- crises, terminus- termini (конечная станция), criterion- criteria, phenomenon- phenomena, stimulus- stimuli, datum- data (данные, база), medium- media (средство) , formula- formulae, index- indices, antenna- antennae, etc.)
Слайд 12

Compound nouns usually form their plural by adding –s/-es to the second noun. But to the first noun if it is followed by a preposition ( mothers-in-law, passers-by). At the end of the compound if it doesn’t include any nouns (letdowns).
Irregular plurals: man- men (but: Walkmans), woman- women, foot- feet, tooth- teeth, mouse- mice, louse- lice, child- children, goose- geese, sheep- sheep, deer- deer, fish- fish, trout- trout (форель), cod- cod (треска), salmon- salmon (лосось), ox- oxen, spacecraft- spacecraft, aircraft- aircraft, hovercraft- hovercraft, means- means, species- species, swine- swine, dozen- dozen ( but: in dozens), score- score – счет, задолженность (but: scores of people - множество), series – series, rendezvous- rendezvous.
Слайд 13

Some problems with verb forms
We use singular verb forms with: nouns which refer to school subjects (maths, politics), sports (athletics), games (billiards, dominoes, darts, draughts [drɑːfts] (шашки)), illnesses (measles (корь), mumps (свинка)); when we talk about an amount of money, a time period, weight, distance, etc. ( Five thousand pounds was donated to build a new hospital wing. Two weeks isn’t long to wait. Ten miles is a long way to ride.); with group nouns when we mean the group as a unit ( jury, family, team, group, crew (команда, экипаж), crowd, class, audience, committee, council (совет), army, club, press, government, company, staff (штат), etc.)
Слайд 14

Some problems with verb forms
We use plural verb forms with: nouns which refer to objects that consist of two parts ( trousers, binoculars, shorts, pyjamas, tights, glasses, earrings, scissors['sɪzəz] (ножницы), compasses (циркуль), scales (весы), tongs (щипцы, клещи), jeans, spectacles, etc.); nouns such as: clothes, police, stairs, looks, surroundings (окрестности, окружение), outskirts (окраина), premises (недвижимость), earnings (заработок, прибыль), wages, cattle (скот), poultry (птица), congratulations, thanks, riches, goods (товары), contents (содержание), oats (овес), potatoes, carrots, onions ( but: a potato/a carrot/ an onion); group nouns when we mean the individuals. These nouns are plural in Russian but both singular and plural in English: watch- watches, clock- clocks, gate- gates, sledge- sledges, vacation- vacations ( Our summer vacation lasts 2 months. We have 2 vacations a year.)
Слайд 15

The category of case
We show possession in English with the genitive form of a noun. This means we normally use ‘s (апостроф + s) or ’ (апостроф без s) for people and some living creatures. ( Frank’s car; a boy’s cat; Doris’s address, an actress’s career, children’s games, my father-in-law’s house, the girls’ uniforms). We use ‘s and ‘ with some non-living things: time phrases ( a day’s work, two hours’ journey), the names of countries/ cities/ships ( Moscow’s theaters), nouns expressing space/ weight/organization ( the river’s edge, the company’s success), with the nouns world/ country/city/ship (world’s best museums) . The genitive is used in some set expressions and fixed phrases: for Heaven’s sake (ради Бога), for God’s sake, at one’s wit’s end (стать в тупик), to a hair’s breadth (точь-в-точь), by a hair’s breadth (на волоске от), at a stone’s through, the earth’s surface, journey’s end, etc.
Похожие презентации
 Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland
 London is the capital of GB
London is the capital of GB
 Help about the house
Help about the house
 In the park
In the park
 There is / There are
There is / There are
Поделиться ссылкой на презентацию через:
Код для вставки видеоплеера презентации на свой сайт:

